For in Situ Hybridization Which Probe Must Be Used
They are produced synthetically by an automated chemical synthesis employing a specific DNA nucleotide sequence of your choice. DNA or RNA single stranded or double stranded.
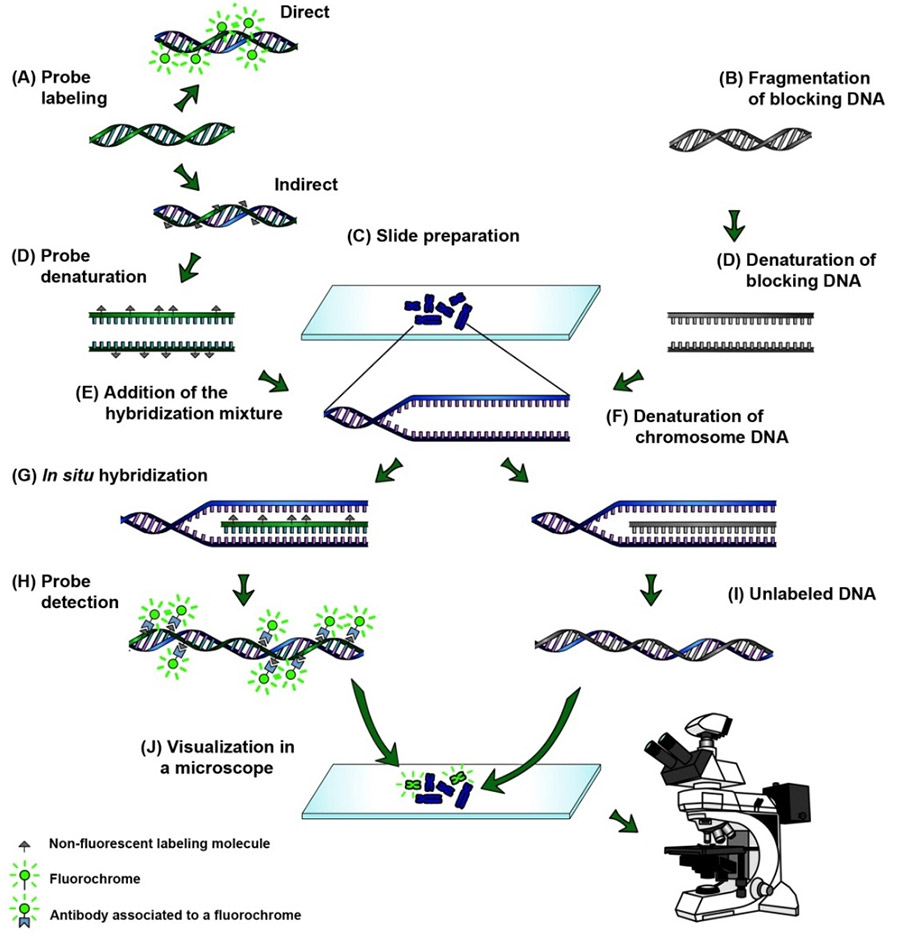
In Situ Hybridization Ish And Fluorescence In Situ Hybridization Fish Creative Diagnostics
A labeled RNA or DNA probe can be used to hybridize to a known target mRNA or DNA sequence within a sample.
. Previously scientists have used radioactive probes for this procedure however with advances in science researchers can now perform an in situ hybridization using non-radioactive probes or even. A second control probe that can be used is 3H-polyU. In situ hybridization ISH is a type of hybridization that uses a labeled complementary DNA RNA or modified nucleic acids strand ie probe to localize a specific DNA or RNA sequence in a portion or section of tissue in situ or if the tissue is small enough eg plant seeds Drosophila embryos in the entire tissue whole mount ISH in cells and in circulating tumor cellsCTCs.
In this chapter we provide a systematic overview of the published guidelines and validation procedures for fluorescence in situ hybridization FISH probes for clinical diagnostic use. Linearize this plasmid by digesting at or ahead of the 3 of cloning site. 7- Try to increase the hybridisation temperature if you see any.
Labeled ssDNA or ssRNA probes are used to hybridize with in vivo mRNA or DNA that is denatured to become ssDNA prior to hybridization. In situ hybridization The methods used to localize mRNA or single-stranded ss DNA at the tissue or cellular level. Set up an In-vitro Transcription reaction with T7 polymerase or whatever corresponds to the promoter you used.
In situ hybridization is a laboratory technique in which a single-stranded DNA or RNA sequence called a probe is allowed to form complementary base pairs with DNA or RNA present in a tissue or chromosome sample. In situ hybridization indicates the localization of gene expression in their cellular environment. Clone the DNA that will give rise to the probe downstream of T7 or any other promoter.
This control is used to describe the distribution of total polyA RNA in the tissue and to assess whether the RNA within a cell is. The most commonly used probes for the diagnosis of hematolymphoid lesions include Epstein-Barr virus early RNA EBER and immunoglobulin light chains κ and λ. This labeled RNA or DNA probe can then be detected by using an antibody to detect the label on the probe.
Is used for the detection of early RNA transcript of Epstein-Barr Virus EBV infection. Hybridization cocktail is used to control chemical environment of probe and tissue during reaction. In Situ Hybridization Testing.
The optimal hybridization temperature depends on several factors including the types of bases in the target sequence and the concentration of certain ingredients in the media. All theoretical aspects are covered as well as some practical examples from the authors experience. In situ Hybridization ISH is a method that allows to localize and detect nucleic acid sequences within structurally intact cells or morphologically preserved tissues sections.
Thus in situ hybridization describes a technique whereby a single strand of nucleotides is used as a probe to recognize and bind to its complementary strand of DNA. The term in situ means in the original place while hybridization refers to a hybrid composed of one strand of DNA with a complementary strand of nucleotides which is referred to as a probe. Buffer to control pH.
DNA probes DNA probes provide high sensitivity for in situ hybridization. In situ hybridization for EBER is the most sensitive and specific technique for demonstration of Epstein-Barr virus EBV in tissues because all infected cells express abundant EBER. Influence assay conditions such as chemical nature label biological specificity.
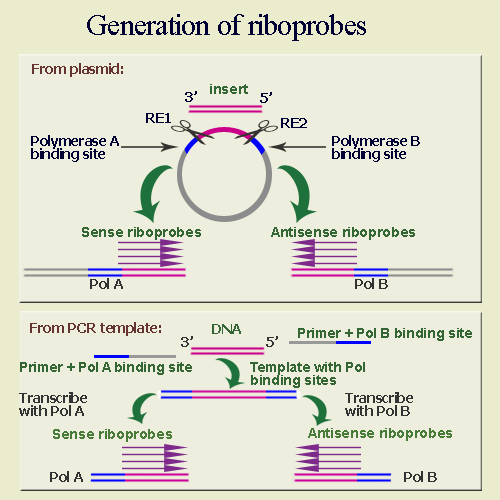
Oligonucleotide probes are usually 2050 bases in length. Probes of this type are called sense mRNA or - strand probes. 5- Try to design probes for different regions of your gene.
The basic principles for. In situ hybridization ISH is a technique that uses colorimetric or fluorescent probes to target and visualize specific DNA or RNA sequences within tissues. An overview is provided concerning the preparation and use of radiolabelled single-stranded RNA probes riboprobes for in situ hybridization.
FISH probes-which are classified as molecular probes or analyte-specific reagents ASRs-have been extensively used in vitro for both clinical diagnosis and research. The use of riboprobes for in situ. Solution that contains the probe can be stored at -20ºC and used again within 2 weeks or more it must be boiled again before use.
Combined with Inform Cytoplasmic mRNA Probe for Lambda the assays assist distinction between polyclonal and monoclonal proliferations of. The best way to store the probe is to aliquot it into working concentrations in Rnase free and siliconized tubes and keep frozen at -20ºC. Is intended to detect cytoplasmic mRNA for Kappa immunoglobulins light chain in tissue.
They do not hybridize as strongly to target mRNA molecules compared to RNA probes so formaldehyde should not be used in the post hybridization washes. The use of riboprobes for in situ hybridization represen. This technology can be broadly applied to study infectious agents cancer or developmental biology.
Like the positive control probe the negative control probe should be similar to the test probe in base pair composition type of nucleic acid ie oligonucleotide double-stranded DNA RNA etc labeling and final concentration. The probes can therefore be used to detect. 6- Try to keep the length of the probe in the range of 400-600 bases.
Templates must be linearized before making a probe though PCR templates can also be used. The probe has a chemical or radioactive label attached to it so that its binding can be observed. Fluorescence in situ hybridization FISH is a kind of ISH which uses fluorescent probes binding parts of the chromosome to show a high degree of sequence complementarity.
In developing an in situ hybridization protocol it is vital to learn optimal temperatures and times needed for formation of the hybrid between the cDNA probe or cRNA probe and unique RNA or DNA in the cell. There are essentially four types of probe that can be used in performing in situ hybridization.
Fluorescent In Situ Hybridization Flow Chart The Samples Are Fixed Download Scientific Diagram
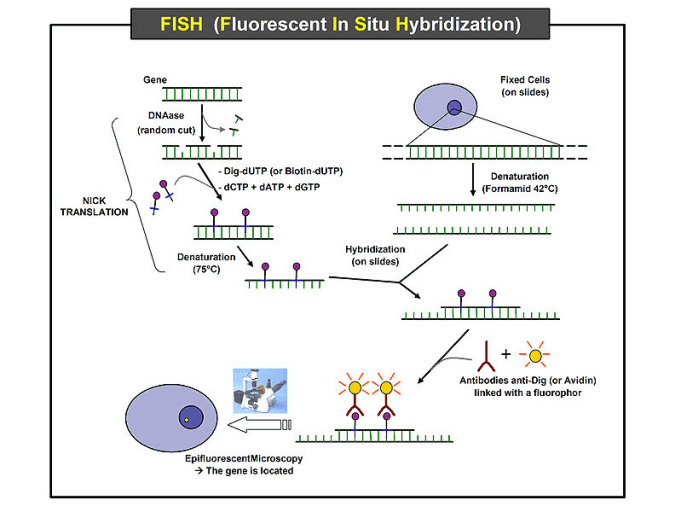
Fluorescence In Situ Hybridization Fish Protocol Creative Biomart
Histological Techniques 5 In Situ Hybridization Atlas Of Plant And Animal Histology
No comments for "For in Situ Hybridization Which Probe Must Be Used"
Post a Comment